Step into the world of ARM Server
What is ARM
ARM with the full name of 'Advanced RISC Machine', is a famous RISC processor from Cambridge England.
CISC vs. RISC
complex instruction set computer: X86 Intel AMDreduced instruction set computer: ARM MIPS Power RISC-V
There are some differences between X86, such as no microcode, no hyper-threading
Why is ARM
It has simplified ISA, better efficient, low cost
AWS, ARM is 40% better on efficient cost,Oracle, provide penny instance with ARM
ARM core architecutre
The ARM core architecture has been developed to V9 today since V1 in 1985.
From Arm V7, it changed its product naming to Cortex, which has below different types:
-
- A: Application
- R: Real-time
- M: Microcontroller
- SC: SecureCore
Its Instruction set Architecture:
-
- AARCH64
- AARCH32
Architecture extension and its features
There is also a microarchitecture under the architecture, Arm will release a new microarchitecture each year.
Armv8.1-A
- Atomic memory access instructions (AArch64)
- Limited Order regions (AArch64)
- Increased Virtual Machine Identifier (VMID) size, and Virtualization Host Extensions (AArch64)
- Privileged Access Never (PAN) (AArch32 and AArch64)
Armv8.2-A
- Support for 52-bit addresses (AArch64)
- The ability for PEs to share Translation Lookaside Buffer (TLB) entries (AArch32 and AArch64)
- FP16 data processing instructions (AArch32 and AArch64)
- Statistical profiling (AArch64)
- Reliability Availability Serviceabilty(RAS) support becomes mandatory (AArch32 and AArch64)
Armv8.3-A
- Pointer authentication (AArch64)
- Nested virtualization (AArch64)
- Advanced Single Instruction Multiple Data (SIMD) complex number support (AArch32 and AArch64)
- Improved JavaScript data type conversion support (AArch32 and AArch64)
- A change to the memory consistency model (AArch64)
- ID mechanism support for larger system-visible caches (AArch32 and AArch64)
Armv8.4-A
- Secure virtualization (AArch64)
- Nested virtualization enhancements (AArch64)
- Small translation table support (AArch64)
- Relaxed alignment restrictions (AArch32 and AArch64)
- Memory Partitioning and Monitoring (MPAM) (AArch32 and AArch64)
- Additional crypto support (AArch32 and AArch64)
- Generic counter scaling (AArch32 and AArch64)
- Instructions to accelerate SHA
Armv8.5-A and Armv9.0-A
- Memory Tagging (AArch64)
- Branch Target Identification (AArch64)
- Random Number Generator instructions (AArch64)
- Cache Clean to Point of Deep Persistence (AArch64)
Armv8.6-A and Armv9.1-A
- General Matrix Multiply (GEMM) instructions (AArch64)
- Fine grained traps for virtualization (AArch64)
- High precision Generic Timer
- Data Gathering Hint (AArch64)
Armv8.7-A and Armv9.2-A
- Enhanced support for PCIe hot plug (AArch64)
- Atomic 64-byte load and stores to accelerators (AArch64)
- Wait For Instruction (WFI) and Wait For Event (WFE) with timeout (AArch64)
- Branch-Record recording (Armv9.2 only)
Armv8.7-A and Armv9.3-A
- Non-maskable interrupts (AArch64)
- Instructions to optimize memcpy() and memset() style operations (AArch64)
- Enhancements to PAC (AArch64)
- Hinted conditional branches (AArch64)
Armv9
V9 is the latest generation which is released from last year, it is more focus on AI and Security, it includes two feature:
-
- SVE2(Scalable Vector Extension)
- CCA arm confidential compute architecture
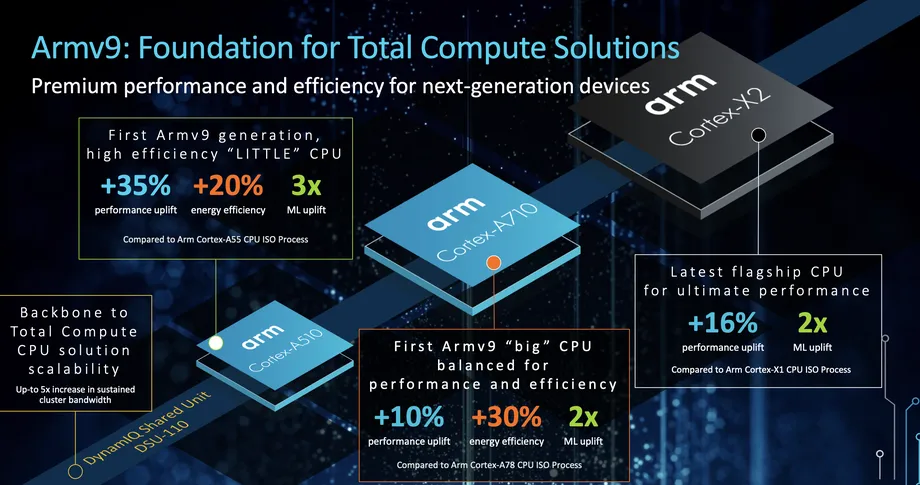
ARM product platform
ARM has two main products, Neoverse and Cortex.
Neoverse focus on cloud and edge computing while cortex on Mobile and Embedded.
Cortex
V8:
Cortex-X1: performance over efficiency
A78C: HPC
A78: VR
A77: Third generation HPC processor, 5G
A76: Second generation HPC processor
A75-55: First generation HPC processor V8.2 DynamIQ
A73:A53
V9:
Cortex-X2
Cortex-A710 big cpu
Cortex-A510 little cpu
Cortex-A310
Neoverse Platform
Code name:
-
- Ares
- Perseus
- Zeus
- Poseidon
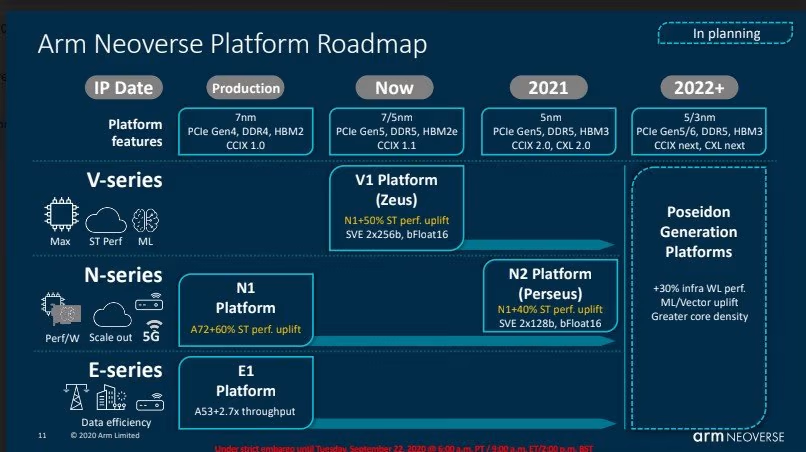
Neoverse platform was introduced in 2018, it has three different directions:
- V for maximum performance
- N for Scale out Performance
- E for efficient throughput
N1: Armv8.2-A Ares

Givation 2
Amperea Altra
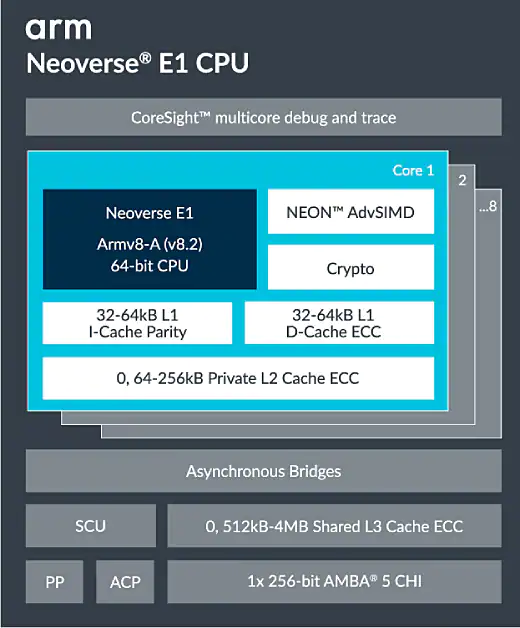
E1 ARM V8.2
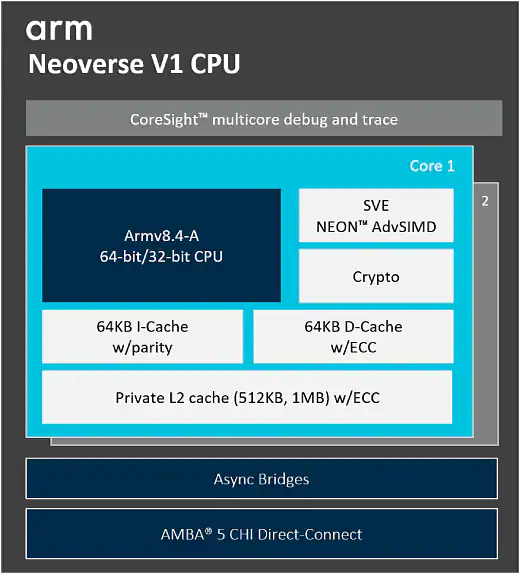
V1 : SVE(first time) + Arm8.4-A Zeus
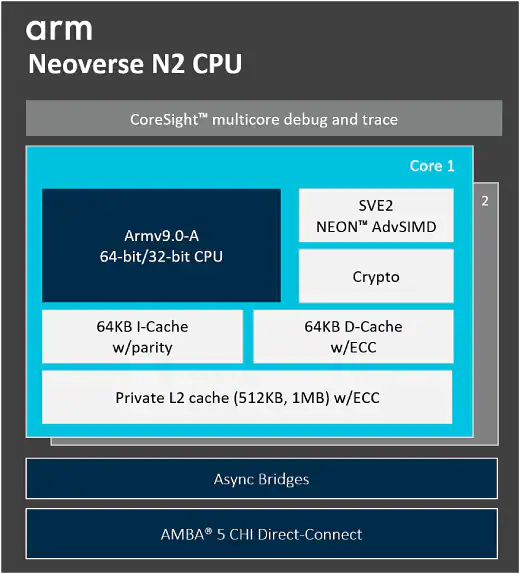
N2: SVE2 + MTE Perseus + Armv9-A
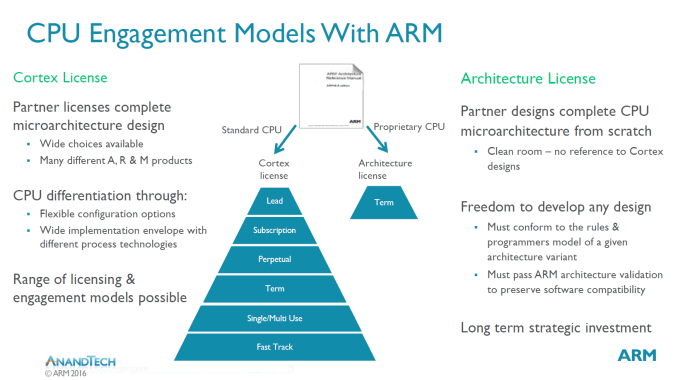
ARM License type
CXC program
In close collaboration with Arm engineering teams, program partners can shape a final CPU product to meet their specific market demands.
ARM Server processor Vendors
Amazon Graviton
Graviton1
2018 Cortex A72
Graviton 2
2019 N1
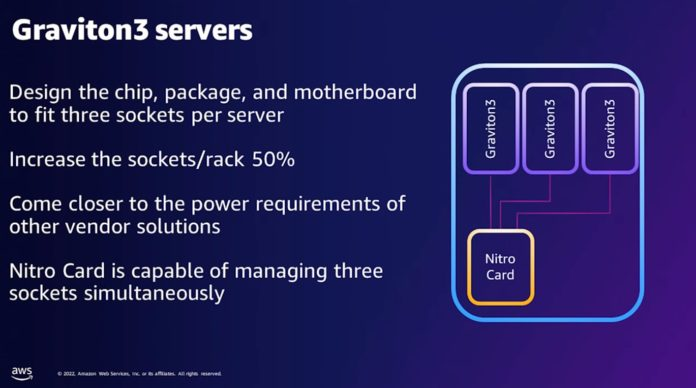
Graviton 3
3 sockets per motherboard, DDR5
AMD Seattle: killed
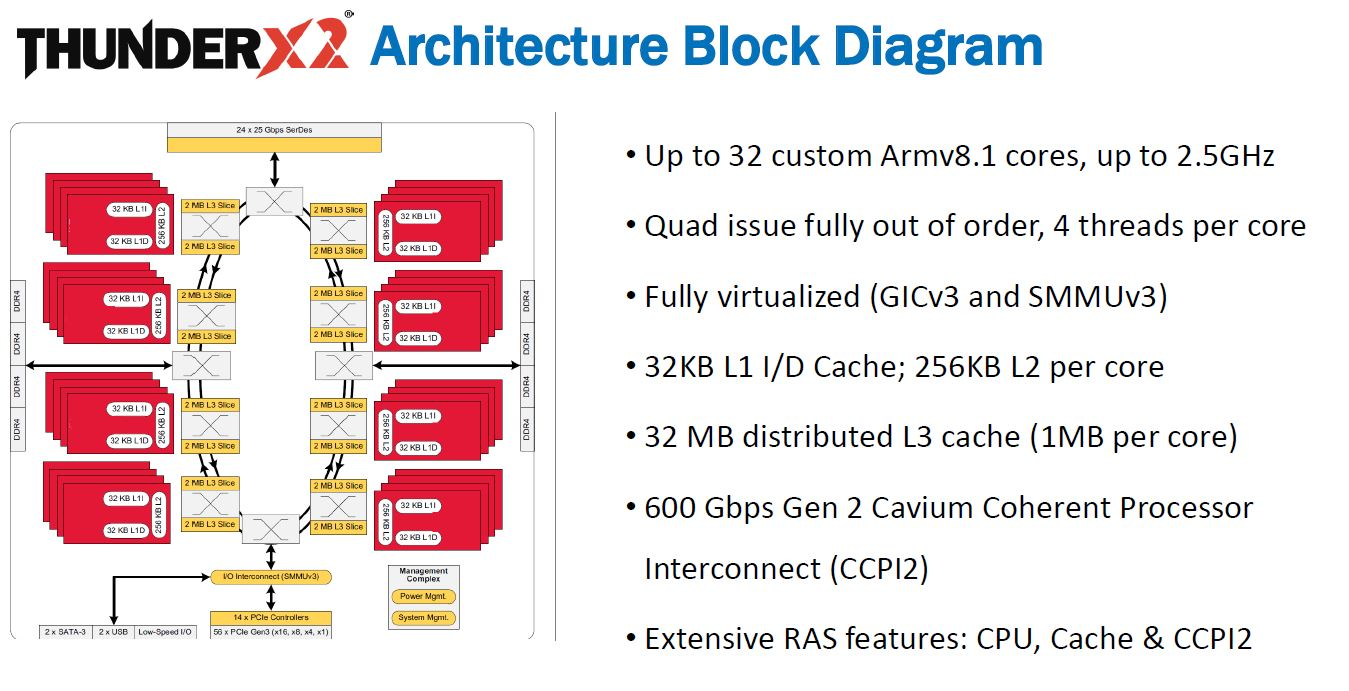
Marvell thunderX
Qcom arm server(Centriq) == >
Broadcom(Vulcan) ==> Cavium(thunderX) ==> Marvell (thunderX)
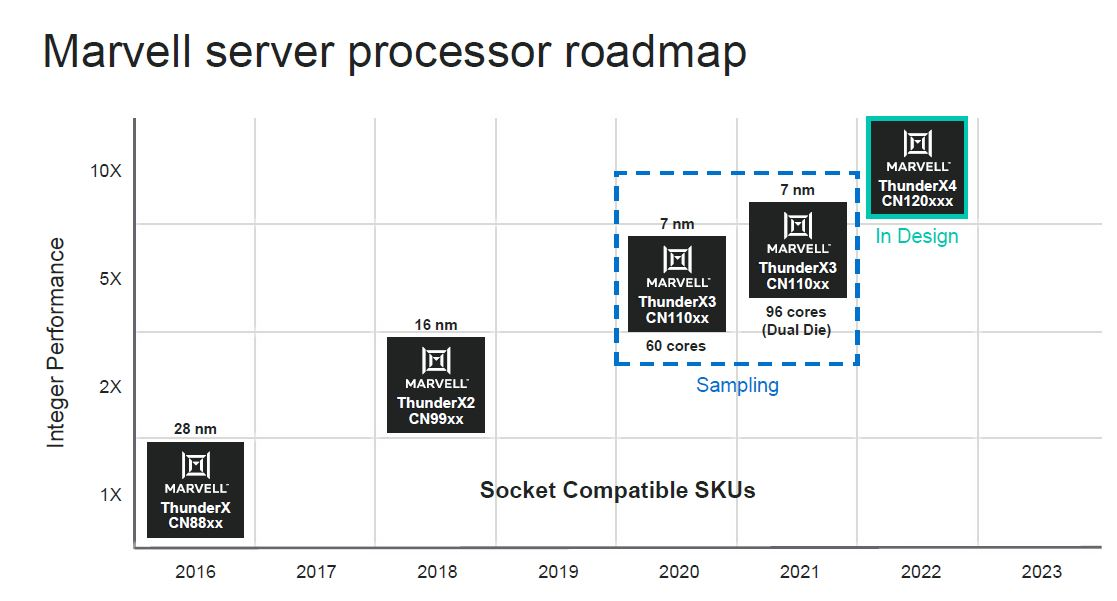
thunderbird2 => thunderbiard3(cancelled) ==>thunderx4
V8.1 v9
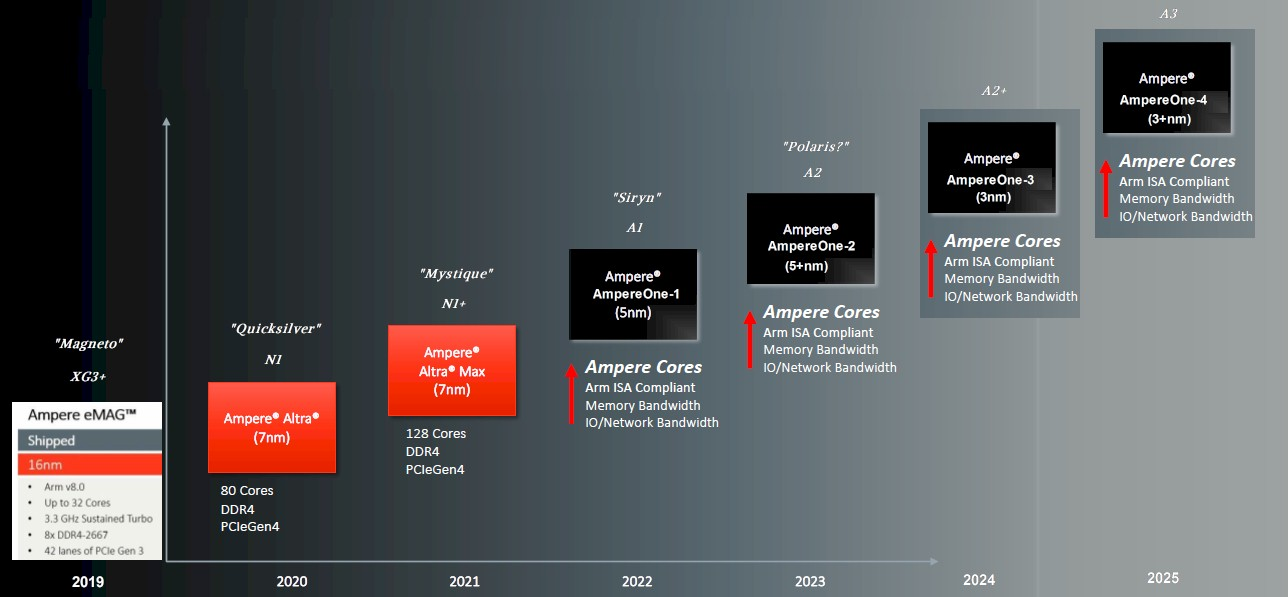
Ampere Computing
Advanced Micro(X-Gene) ==> Ampere Computing
Intel engineers ==>
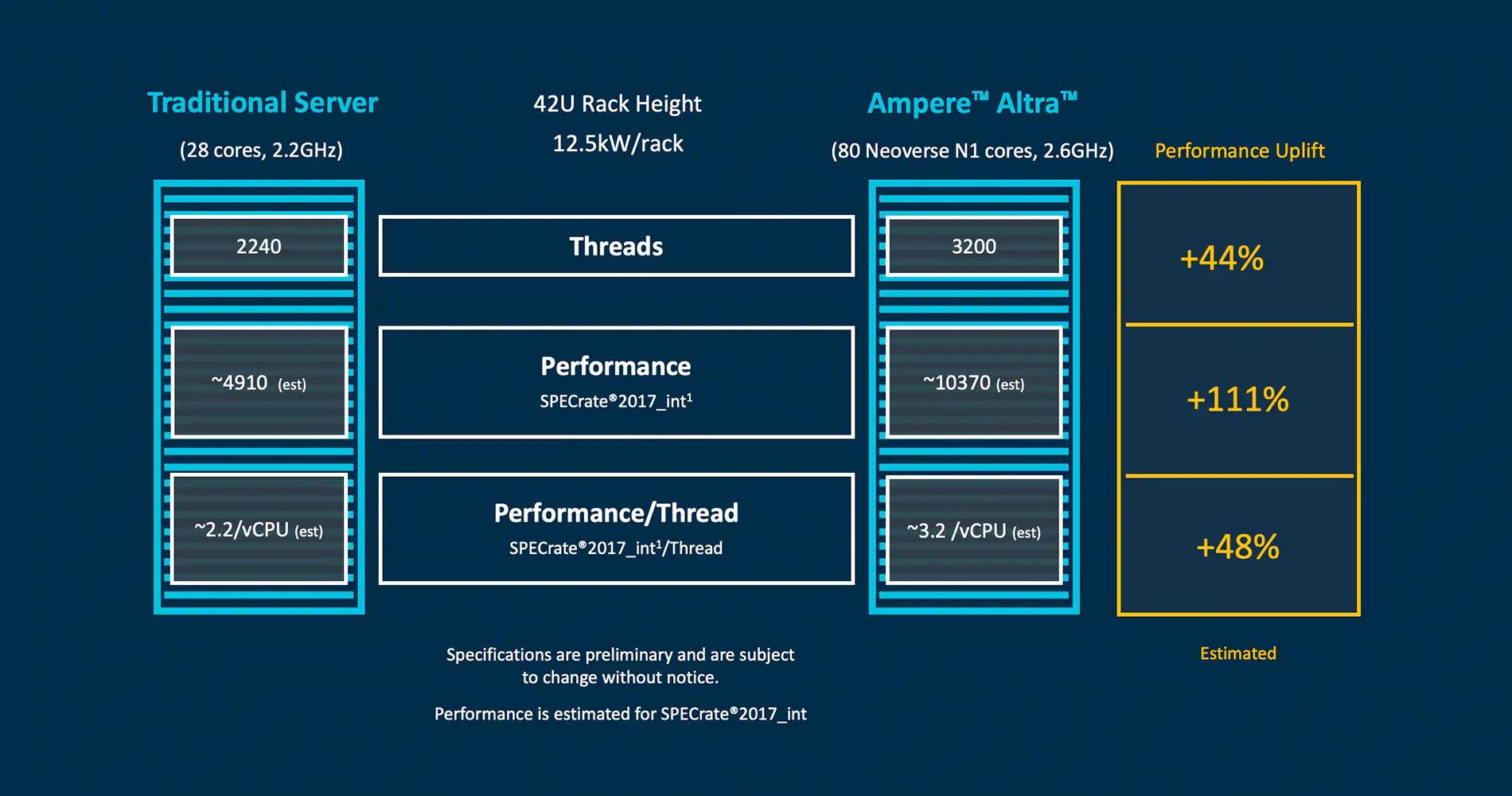
Ampere Altra: V8.2
Parter: GIGABYTE
Altra==>Altra Max
80 ==> 128
Ampere-1 V8.6-A
5nm/PCIe Gen5/DDR5
Nvidia
1. .Denver program(killed)
2. Grace
Armv9 144 cores, dcc5
Two advantages:
1. Grace Hopper SuperChip
cpu + gpu 900 GB/S == 7x PCIE5
2. Work with Bluefield
Fujitsu
A64FX V8.2
Fujitsu supercomputer Fugaku
HPE Apollo
48 cores + V8.2 + SVE
Apple
M2 Pro/Max/Ultra
M2 pro/max/Ultra
M3 in 2023
Cloud Vendors
1. AWS
M6g M6gd
T4g
C6g C6gd C6gn
R6g
X2gd
LM4gn ls4gn
G5g
Azure
Ampere Altra
Oracle
Ampere Altra
ARM Hypervisors
Hardware Virtualization
VHE
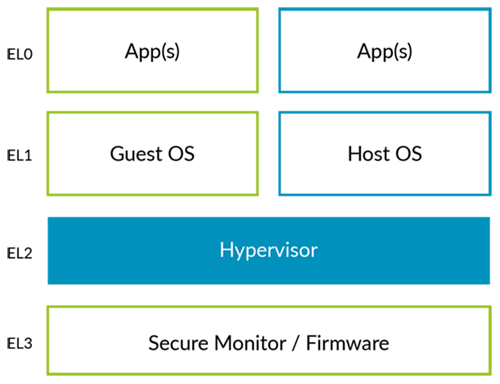
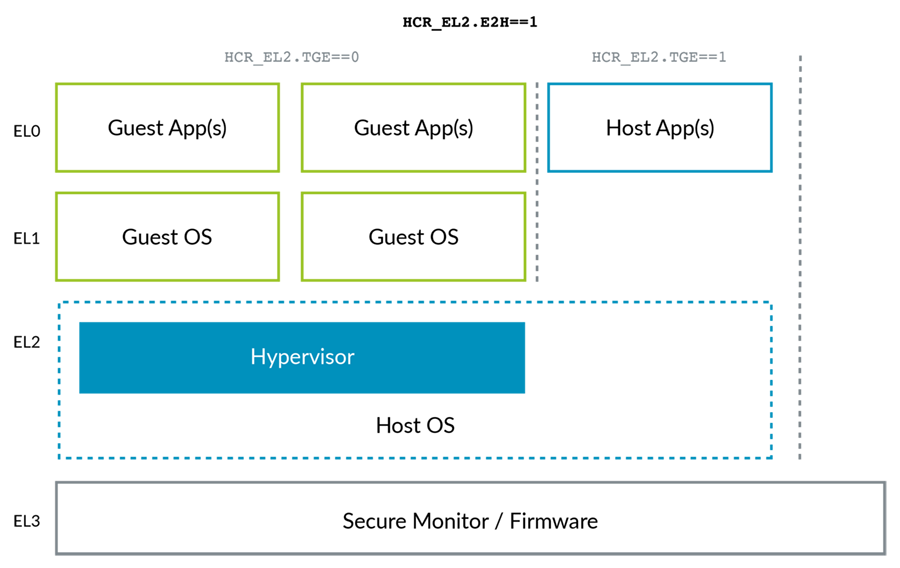
EPT 《==》 Stage2 translation
IOMMU 《==》 SMMU
APICv 《==》GICv
KVM:
vCPUs 123==>512
52bit physical memory 4PB(v5.14)
64K page: mainly discussed in upstream
QEMU:
Firmware: UEFI
Device: VIRTIO-GPU
QEMU machine model
virt generic virtual platform
CPU 'host' for kvm only
sbsa-ref
Server Base System Architecture Reference board
Reference:
https://community.arm.com/arm-community-blogs
https://www.nextplatform.com/2019/12/13/amping-up-the-arm-server-roadmap/
https://www.qemu.org/docs/master/system/arm/virt.html
https://www.qemu.org/docs/master/system/arm/sbsa.htm